A Complete Checklist and Guide on How to Start a Supermarket Business in India – 2025
January 1, 2025

Suppose you are considering venturing into the Indian supermarket industry with small-scale supermarkets or large-scale supermarkets. In that case, it is crucial to create a comprehensive business plan and checklists that consider various factors. The Indian market is highly competitive, and understanding the dynamics of the industry, and outlining essentials is important to ensure a smooth and profitable operation.
In this article, we have covered comprehensive requirements on how to start a supermarket business in India including a business registration checklist, key licenses, documentation requirements, location checklist, operational requirements, SOPs, and software applications required for a successful supermarket business.
After thorough research we have created a checklist that will serve as a roadmap, ensuring smooth establishment of your supermarket business.
As a retailer or entrepreneur, you may be wondering how to start your supermarket business in India. In recent years, with business-friendly policies of the government towards organized businesses, it has become easier to start and flourish your supermarket business. With the right steps and meticulous attention to the below checklists, you can start a supermarket in the fastest and frictionless way.
Follow the below steps and checklists to start your own supermarket:

It is imperative to define and determine the size and scale of the supermarket, the required capital, and financing options. Below are the key considerations:

To kickstart your supermarket venture, you will need to obtain a business registration. You can register your business entity as a sole proprietorship, partnership, one-person company, limited liability partnership, or private limited company. This formal registration gives your business legal recognition which is mandatory for such a business, and instills confidence in customers and stakeholders.
Securing a Shop and Establishment License is essential for protecting the rights and interests of your supermarket’s workforce. This license regulates terms and working conditions, ensuring a safe and fair environment for employees. Obtaining this license is a legal mandate for any retail establishment in India.
A practical, easy-to-follow checklist to help you launch your store the right way.
If your supermarket’s aggregate business turnover exceeds Rs 40 lakhs (or Rs 20 lakhs in special states), registering under GST is mandatory. This ensures compliance with tax regulations and establishes your business as a legitimate entity in the eyes of the government. Supermarkets having multiple branches or locations may also be required to individually register for GST for each branch if they function as independent business entities.
The tax is levied on the income or salary earned by employees as compensation for their services to the company. It is a requirement for all businesses and self-employed individuals. The amount of professional tax depends on the rules set by the respective state governments. Some states do not mandate PT registration. It is necessary to comply with the filing of returns and make the payment of professional tax on a monthly or annual basis, depending on its applicability.
Documentation Requirements:
Various documents are necessary to fulfill the legal prerequisites for opening a supermarket.
These include:

Finding the right location that favors business outcomes and designing the most feasible and efficient layout are pivotal components in the blueprint of a successful supermarket venture. Through thorough research, prioritize areas with high-middle-class residents, minimal supermarket competition, and considerable foot traffic to maximize market penetration.
Beyond demographics, practical considerations such as ample parking and storage space for stock are vital for smooth operations. When finalizing the location, factor in rent or purchase prices to align with the budget. Design a clear and precise layout that organizes products by category, ensuring aisles have enough space for customers with trolleys and baskets to navigate freely.

In the dynamic and competitive landscape of the supermarket business, the implementation of robust Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) is paramount for sustained success. SOPs serve as the guiding framework, akin to meticulously crafted flowcharts, delineating tasks and processes for diverse scenarios that may unfold in the supermarket environment.
SOPs are designed to enable different departments to function harmoniously by recognizing and addressing interdependencies that naturally arise within supermarket operations. SOPs act as a proactive measure to identify and mitigate potential operational challenges, paving the way for streamlined day-to-day activities and reducing disruptions.
SOPs serve as a blueprint for error reduction by offering employees a clearly defined path to follow. This not only minimizes mistakes but also ensures consistency in processes throughout the supermarket.
Components of Supermarket SOPs:
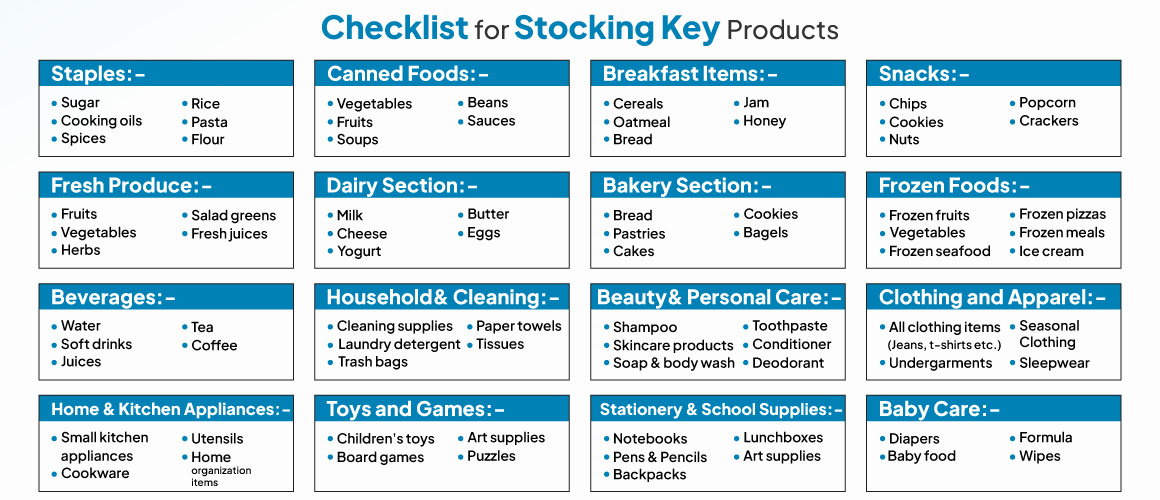
This checklist outlines essential steps for ensuring that a supermarket maintains a well-curated selection of products. Later identifying top-selling items as per customer needs and preferences and seasonal sales is critical for avoiding stock outs and keeping optimal stock levels.
The most essential products that supermarkets need to stock are listed below:

In the modern era of supermarket management, the role of software applications, particularly Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Integrated Point of Sale (POS) systems are indispensable for achieving seamless operations and facilitating sustainable growth. To ensure the effectiveness of these software applications, a comprehensive checklist is essential. This checklist serves as a guide for supermarkets aiming to harness the power of data synchronicity and analysis to drive informed decision-making and successful expansion.
Before you choose any software provider or software application for your supermarket keep the following points in mind:

Utilize both traditional and digital channels to create a comprehensive marketing plan:
Understanding the market is key to developing a viable pricing strategy:
Determine the number of employees required based on the size and scale of your supermarket. Develop a robust recruitment strategy to attract qualified and committed staff, ensuring the smooth operation of your business.
Opening a supermarket in India requires careful consideration of legal, financial, and operational aspects. The checklists provided in this article will help aspiring businesses navigate the intricacies of the supermarket retail industry. For customer satisfaction, and optimal productivity and efficiency, leveraging technology like Cloud-based Supermarket software is vital. By following this checklist and adapting to the ever-changing market dynamics, you can establish a thriving supermarket business in India and contribute to the nation’s retail sector.

If you are looking for desktop software or mobile appli...
August 8, 2023

https://youtube.com/shorts/Xt4k7UyNnLE?si=lQVNG12dCjo59...
July 17, 2023
